LAMP stands for Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP/Perl/Python. It is a popular stack of open-source software used to create web servers and deploy web applications. In this guide, you’ll learn the step-by-step process for setting up a LAMP stack on the Kamatera cloud platform for the purposes of web development.
Here’s a brief overview of each component:
- Linux: The operating system.
- Apache: The web server software.
- MySQL/MariaDB: The database management system.
- PHP/Perl/Python: The programming languages used for server-side scripting.
Prerequisites
There are three ways to get your LAMP stack working.
- Using a pre-built image
- Using Windows
- Using Ubuntu
Before you begin, ensure you have one of the following sets of software installed on your system:
- Windows 10 or Windows Server and XAMPP (a software bundle that includes Apache, MySQL, and PHP)
- Linux
Using pre-built image
On the homepage, find the “Login” button located at the top right corner.
- Click on the “Login” button.
- Enter your registered email address and password in the provided fields.
- After entering your credentials, click the “Log In” button to access your Kamatera account dashboard.
- Once logged in, you will be directed to the main dashboard of your Kamatera account.
- From the left-hand side navigation menu, click on “My Cloud” to view and manage your cloud services.
- Within the “My Cloud” section, go to “Create New Service” button.
- Click on the “Create New Service” button to start the process.
- Choose the zone that is closest to your target audience.
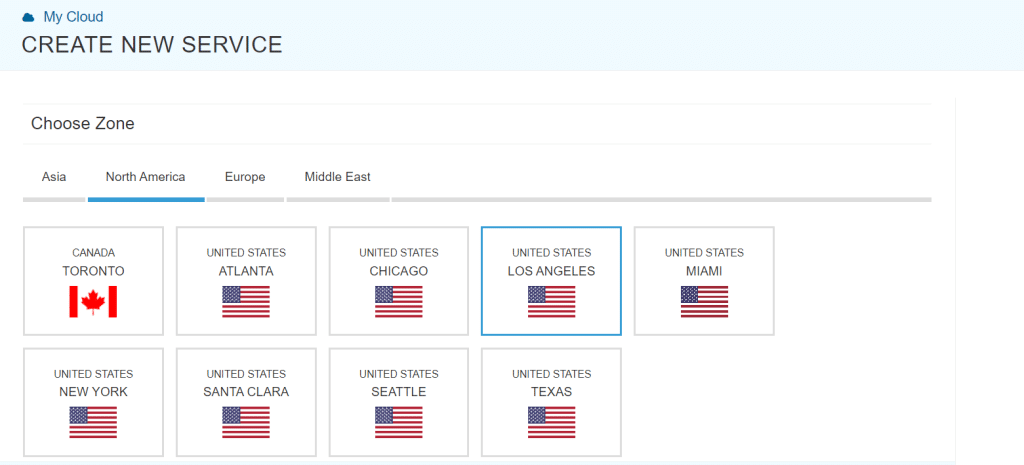
- After choosing the zone, you will continue with the setup by selecting the specifications for your virtual machine.
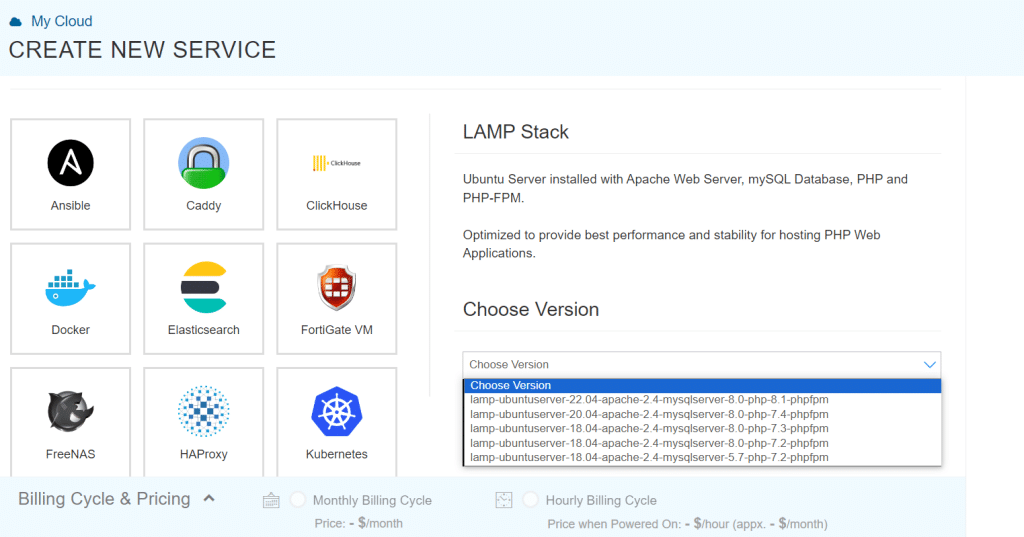
- Choose Service here as shown below.

-
- From the drop-down menu select the version once you have selected the service.
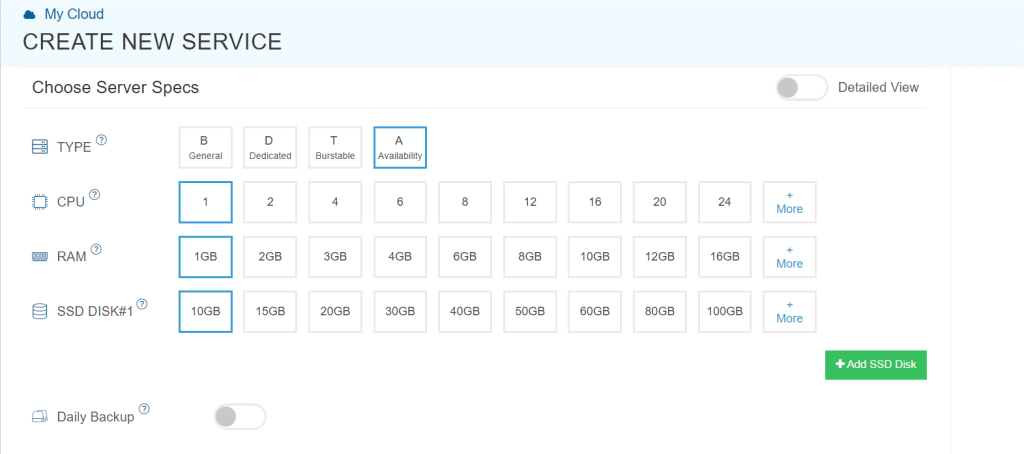
- Choose Server specifications.
Select the Type, CPU, RAM, and NVMe SSD DISK#1 according to your needs.
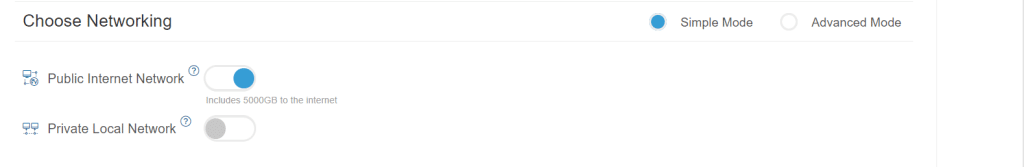
- Choose Networking as Public Internet Network
Advanced Configuration
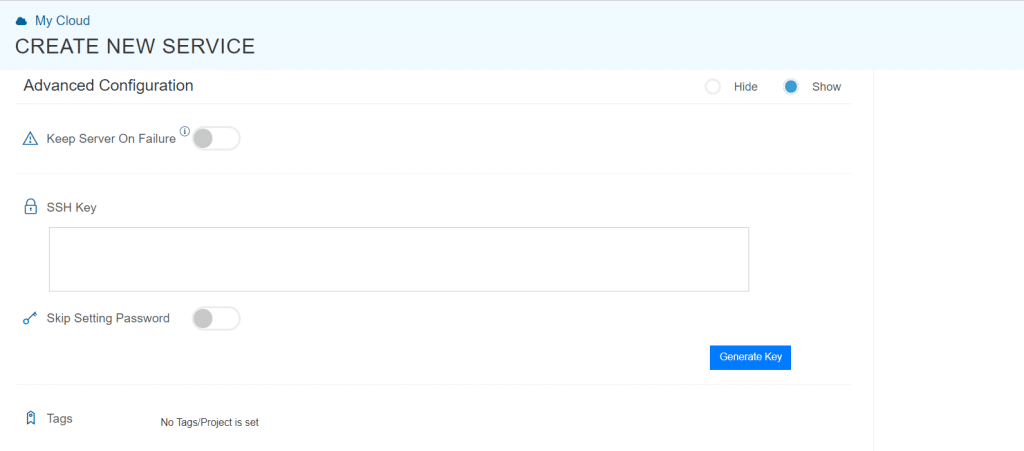
Finalize Settings
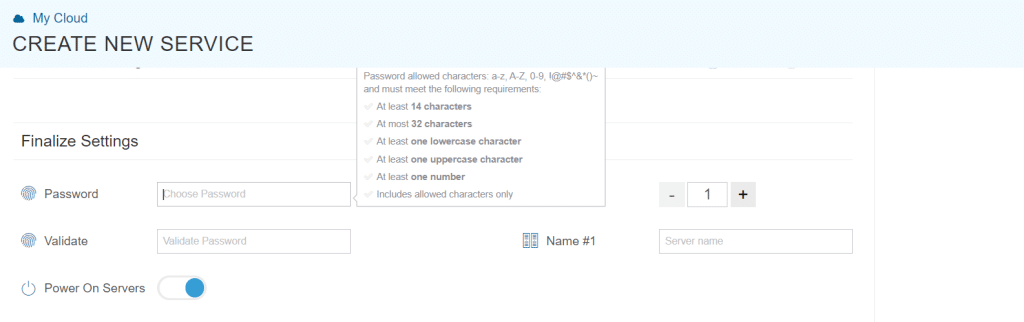
Create a unique password for your server and confirm it by entering it again.
Select a name for your server.
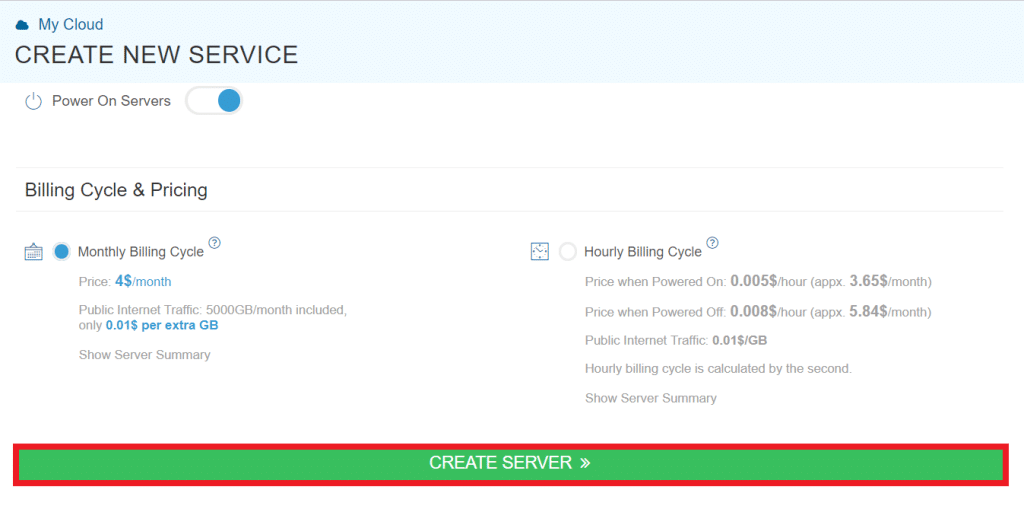
- Click the “Create Server” button to finalize and launch your new virtual machine.
Using Windows
LAMP can be installed on Windows, but it requires a series of steps.
Installing XAMPP
-
- Download the latest version of XAMPP from the official website.
- After the download is complete, run the installer.

- Follow the prompts provided by the installer to install XAMPP on your system.

4. Once the installation process is finished, launch the XAMPP Control Panel.
Configuring Apache
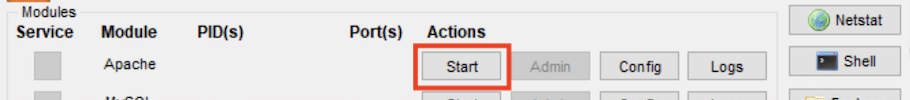
- In the XAMPP Control Panel, locate the Apache section.
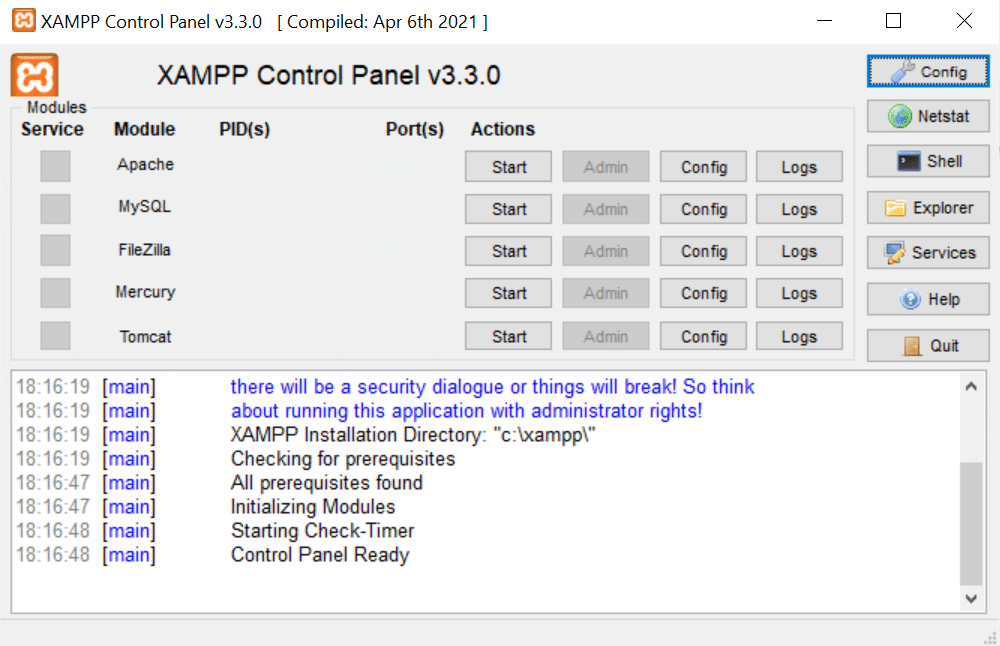
2. Click on the “Start” button next to Apache to initiate the Apache service. Status will be seen changing into ‘running’.
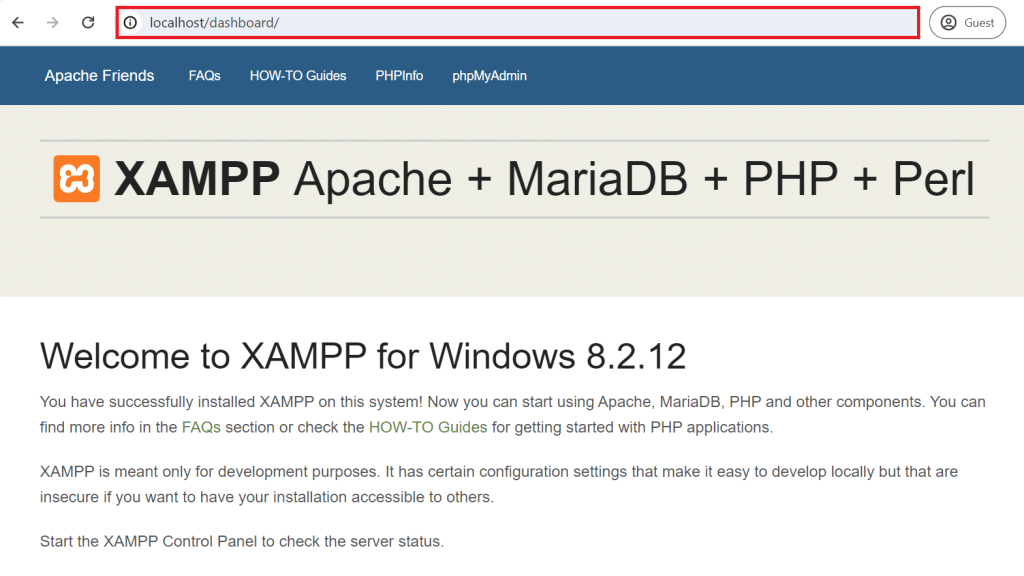
3. Open your web browser and type “http://localhost” into the address bar.
4. Press Enter to navigate to the localhost address.
5. Ensure that Apache is running correctly by verifying that the XAMPP welcome page appears in your browser.
Configuring MySQL
-
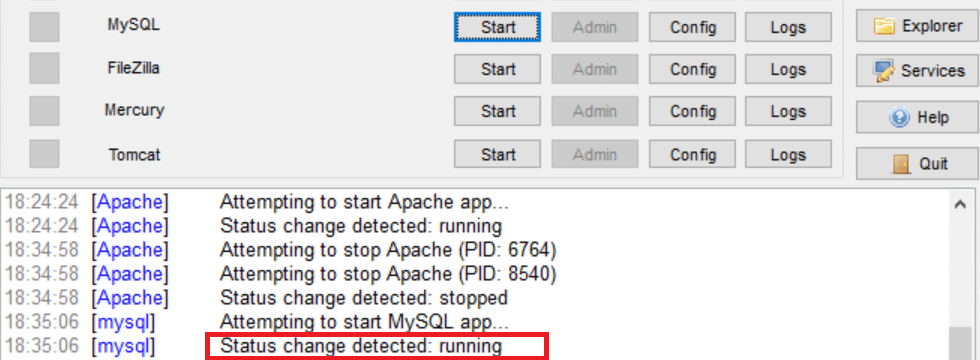
- In the XAMPP Control Panel, locate the MySQL section.

2. Click on the “Start” button next to MySQL to initiate the MySQL service. Status will be seen changing into ‘running’.
3. To access the MySQL command line, click on the “Shell” button in the XAMPP Control Panel.
4. To access phpMyAdmin, click on the “Admin” button next to the MySQL service in the XAMPP Control Panel.
Configuring PHP
-
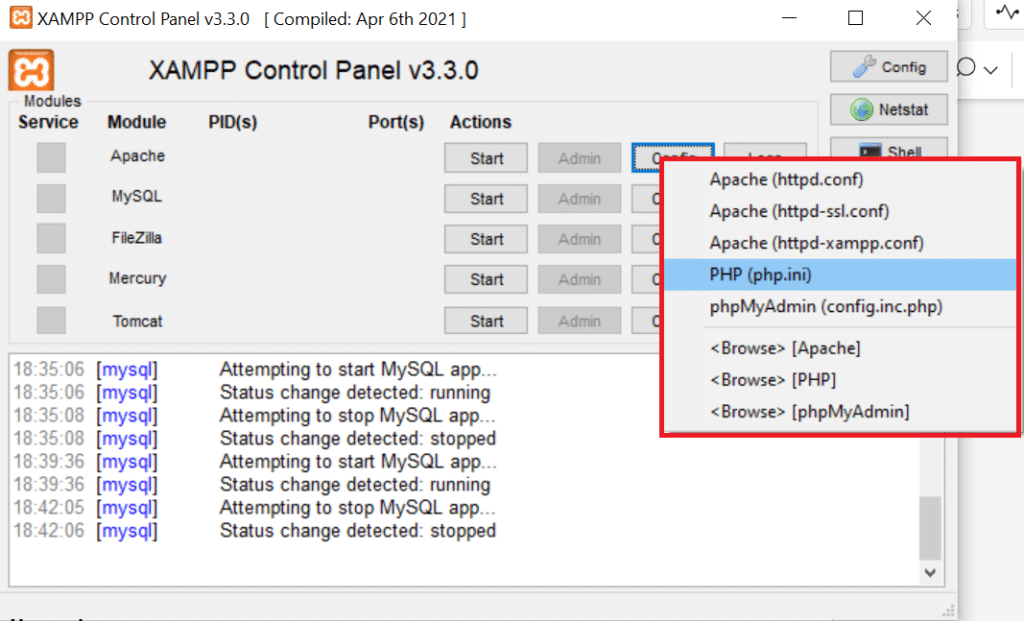
- In the XAMPP Control Panel, locate the Apache section.
- Click on the “Config” button next to Apache.
- From the dropdown menu, select “php.ini” to access the PHP configuration file.
4. Inside the php.ini file, locate the line “; extension=MySQL”.
5. Remove the semicolon “;” at the beginning of the line to uncomment it.
6. Save the changes made to the php.ini file.
7. Restart Apache to apply the changes.
Using Ubuntu
Step 1: Installing Linux
If you haven’t already, install a Linux distribution like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian. For this guide, we’ll use Ubuntu as an example.
Step 2: Update Your Package Manager
- Open a terminal window on your Linux system.
- To ensure you have the latest software, update your package manager by running the following command:
- This will update the list of available packages and upgrade the installed packages to their latest versions.
A LAMP stack is a development framework that comprises four key components: Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. Below are step-by-step instructions for setting up a LAMP stack on Ubuntu:
*Note: These instructions are tailored for a fresh installation of Ubuntu. Ensure your system is up-to-date by executing the following commands in a terminal:
lsb_release -a cat /etc/os-release uname -a
Step 1: Installing Apache
Apache is required for the site visitors to see web pages. Apache is a popular web server with a large active user base that we will install on ubuntu using apt package manager.
-
- Open a terminal window by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T.
- Install Apache by running the following command.
sudo apt install apache2
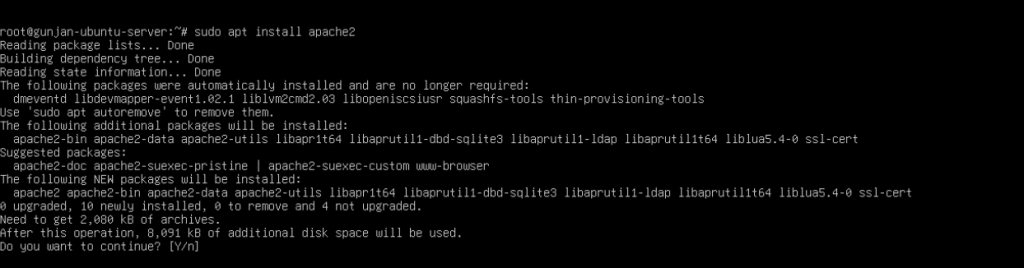
3. Once the installation is complete, enable Apache to start at boot and start the service by executing the following commands.
sudo systemctl enable apache2
sudo systemctl start apache2

4. To verify that Apache is working properly, open a web browser and enter your server’s IP address or “http://localhost” if you’re setting this up on your local machine. You should see the default Apache welcome page.
Step 2: Install MySQL
With a web server set up successfully, a database system needs to be installed for storing and managing site data. MySQL is one such popular and effective database management system used alongside the PHP ecosystem.
-
- Install MySQL by executing the following command.
sudo apt install mysql-server
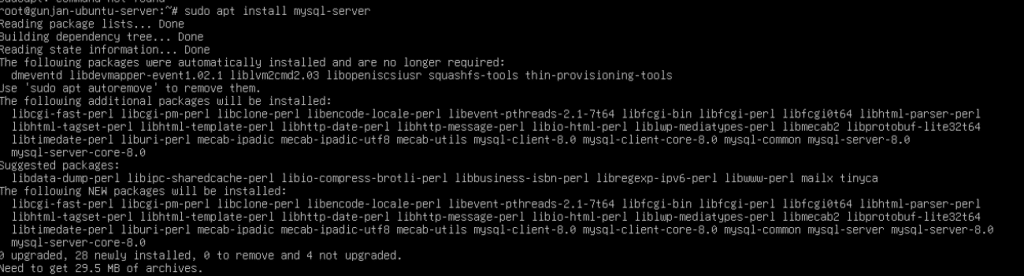
2. During the installation, you will be prompted to set a root password for MySQL. Choose a strong password and remember it.
3. After installation, secure your MySQL installation by executing the following command and following the prompts:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
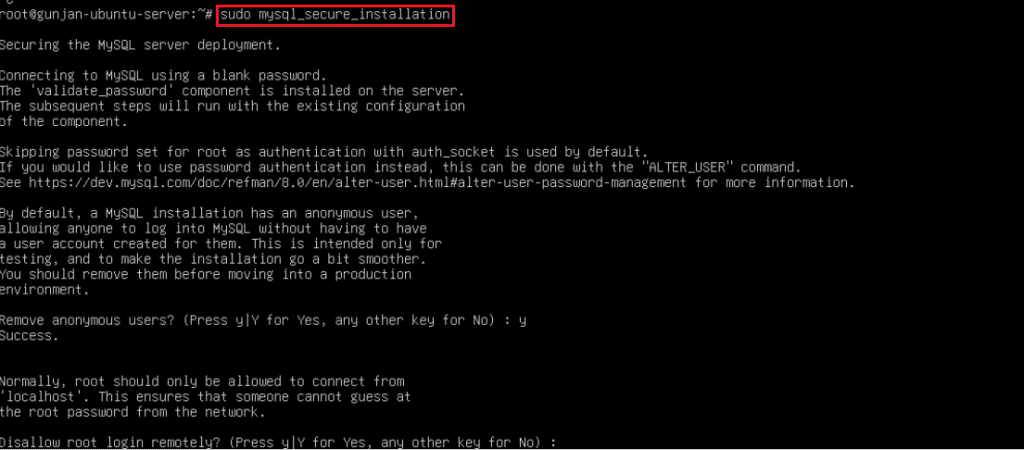
Step 3: Install PHP
With Apache and MySQL installed to host, store and manage the data for your site, PHP is to be installed to serve the code and generate dynamic content for the web server.
-
- Install PHP and some common extensions by executing the following command.
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql
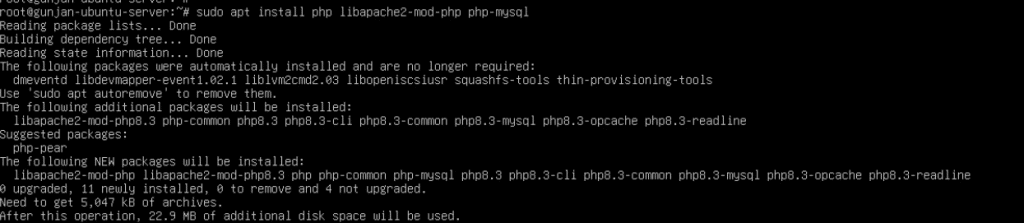
2. Once PHP is installed, you can also test it by creating a PHP info file. To do this, create a new file in the web server’s root directory.
sudo nano /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
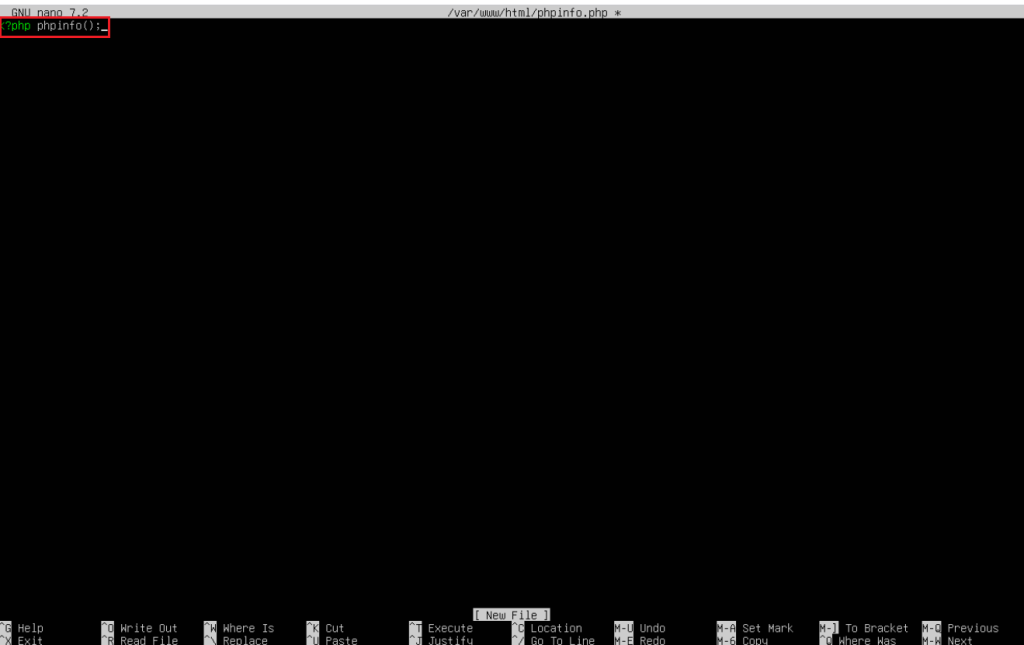
Note: Add the following content to the file and save it:
<?php phpinfo();
3. Restart Apache to apply the changes by executing the following command.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
4. In your web browser, navigate to http://localhost/phpinfo.php (or use your server’s IP address if it’s remote). You should see the PHP information page displayed.
Step 4: Testing MySQL and PHP
You can create a simple PHP script to test the connection to MySQL by following these steps.
- Create a test PHP file by executing the following command.
sudo nano /var/www/html/test-mysql.php
2. Add the following PHP code to the file and save it.
```php <?php $connection = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "your_mysql_password");
if (!$connection) {
die("Database connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
echo "Connected to MySQL successfully!";
mysqli_close($connection); ?>
```
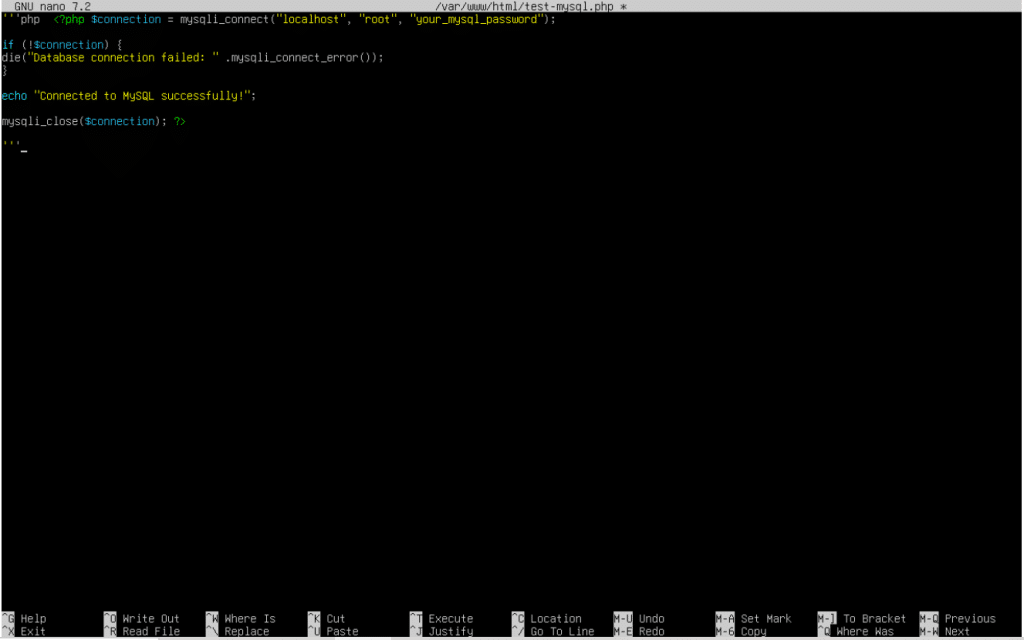
3. Replace ”your_mysql_password” with the root password you set during the MySQL installation in the PHP code.
4. Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost/test-mysql.php (or your server’s IP address). You should see a message indicating a successful MySQL connection displayed in the browser.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed a LAMP stack on your Ubuntu system. You are now ready to start building and hosting web applications on your server.
